Exercise 8 overview of the skeleton – Embarking on Exercise 8: Overview of the Skeleton, we delve into the intricate workings of the skeletal system, a remarkable framework that supports, protects, and facilitates movement within the human body.
This comprehensive guide explores the composition, functions, and structure of the skeleton, examining the diverse roles of bones and the joints that connect them. Furthermore, we investigate the significance of exercise, nutrition, and common skeletal conditions in maintaining optimal bone health.
Overview of the Skeletal System: Exercise 8 Overview Of The Skeleton
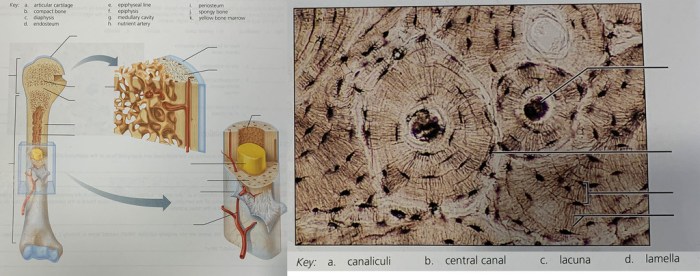
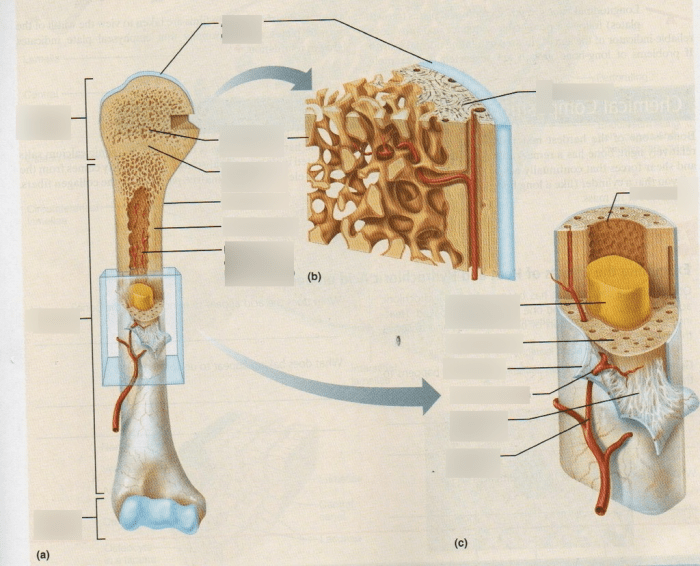
The skeletal system is a complex network of bones and cartilages that provides support, protection, and mobility to the body. It comprises approximately 206 bones, each with a unique structure and function.
Bones are composed primarily of calcium phosphate, which provides rigidity and strength. They also contain collagen, a protein that provides flexibility and resilience. The skeletal system works in conjunction with muscles and joints to facilitate movement, protect vital organs, produce blood cells, and store minerals.
Types of Bones
- Long bones: These are the long, cylindrical bones found in the limbs. They provide support and allow for movement.
- Short bones: These are the small, cube-shaped bones found in the wrists and ankles. They provide stability and support.
- Flat bones: These are the thin, broad bones found in the skull, ribs, and pelvis. They provide protection and support.
- Irregular bones: These are the bones that do not fit into any other category, such as the vertebrae and the facial bones. They have complex shapes and serve a variety of functions.
Functions of the Skeletal System, Exercise 8 overview of the skeleton
- Support: The skeletal system provides structural support to the body, allowing it to stand upright and move efficiently.
- Protection: The bones of the skull, rib cage, and pelvis protect vital organs from injury.
- Movement: The skeletal system works with muscles to facilitate movement. Bones provide leverage for muscles to pull against, enabling a wide range of motions.
- Blood cell production: The bone marrow, located within the cavities of bones, produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Mineral storage: Bones store minerals, primarily calcium and phosphorus, which can be released into the bloodstream when needed.
FAQ
What is the primary function of the skeletal system?
The skeletal system serves multiple functions, including providing structural support, facilitating movement, protecting vital organs, producing blood cells, and storing minerals.
How does exercise impact bone health?
Regular weight-bearing and resistance exercises stimulate bone growth, increasing bone density and reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
What are some common skeletal conditions?
Osteoporosis, arthritis, and fractures are common skeletal conditions that can affect bone health and mobility.