Receptacles listed as tamper-resistant are not required in certain locations, according to the National Electrical Code (NEC). This requirement aims to enhance electrical safety by preventing accidental contact with live electrical parts, particularly in areas accessible to children. However, there are specific exceptions to this rule, where tamper-resistant receptacles are not mandated.
The NEC Artikels specific locations where tamper-resistant receptacles are not required, such as industrial settings, commercial kitchens, and outdoor areas. These exemptions consider the unique characteristics and safety concerns associated with each location.
Tamper-Resistant Receptacle Requirements
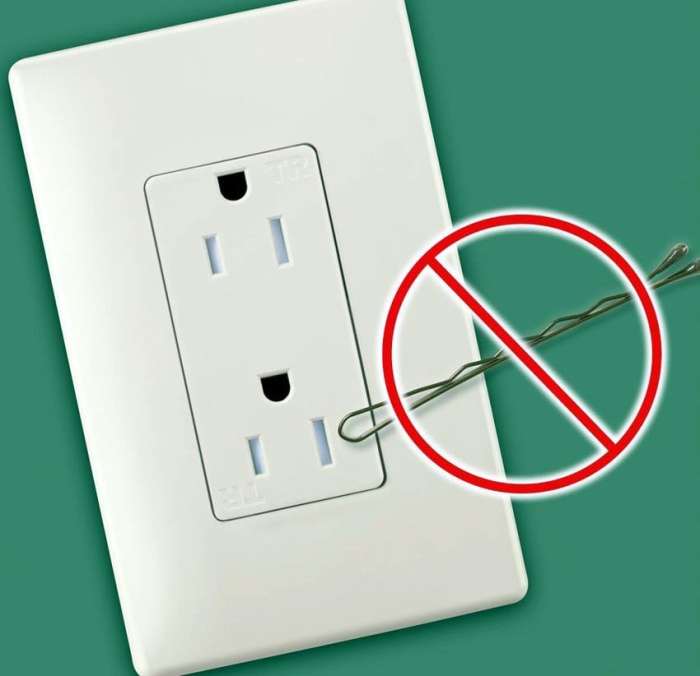

The National Electrical Code (NEC) requires tamper-resistant receptacles (TRRs) in all 120-volt, 15- and 20-ampere outlets in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. TRRs are designed to prevent children from inserting objects into the outlets, which can cause electrical shocks or fires.
Exceptions to the Tamper-Resistant Receptacle Requirement, Receptacles listed as tamper-resistant are not required in
The NEC provides several exceptions to the TRR requirement, including:
- Outlets that are located more than 5 feet above the floor
- Outlets that are used for appliances that are permanently plugged in, such as refrigerators and stoves
- Outlets that are located in industrial settings where they are not accessible to children
- Outlets that are located in outdoor areas where they are exposed to the elements
Locations Where Tamper-Resistant Receptacles Are Not Required
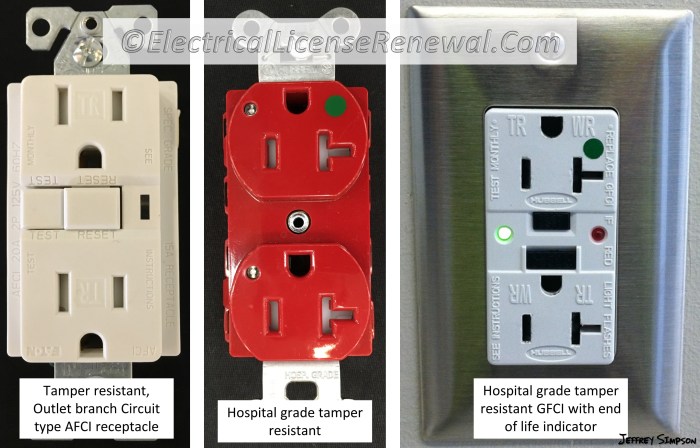

The following are specific locations where TRRs are not required:
- Outlets that are located in unfinished basements or attics
- Outlets that are located in garages or workshops
- Outlets that are located in crawl spaces or other areas that are not accessible to children
- Outlets that are located in industrial settings where they are not accessible to children
- Outlets that are located in outdoor areas where they are exposed to the elements
These locations are exempt from the TRR requirement because they are not typically accessible to children.
Rationale for Exemptions
The NEC provides exemptions for TRRs in certain locations because the safety concerns that are addressed by TRRs are not present in those locations. For example, outlets that are located more than 5 feet above the floor are not accessible to children, so there is no need for TRRs.
Similarly, outlets that are used for appliances that are permanently plugged in are not accessible to children, so there is no need for TRRs.In industrial settings, outlets are often located in areas that are not accessible to children. Therefore, there is no need for TRRs in these locations.Outlets
that are located in outdoor areas are exposed to the elements, which can damage TRRs. Therefore, there is no need for TRRs in these locations.
Impact on Electrical Installations
If TRRs were required in all locations, it would have a significant impact on electrical installations. The cost of installing TRRs would increase, and the safety benefits would be minimal. In addition, TRRs can be difficult to install in some locations, such as in older homes with narrow walls.The
NEC provides exemptions for TRRs in certain locations because the safety concerns that are addressed by TRRs are not present in those locations. Therefore, it is not necessary to require TRRs in all locations.
Alternative Safety Measures
There are a number of alternative safety measures that can be implemented in locations where TRRs are not required. These measures include:
- Outlet covers
- Cord shorteners
- Safety plugs
- Electrical outlet locks
These measures can help to prevent children from inserting objects into outlets, which can cause electrical shocks or fires.
Clarifying Questions: Receptacles Listed As Tamper-resistant Are Not Required In
Why are tamper-resistant receptacles not required in industrial settings?
Industrial settings often involve the use of specialized equipment and machinery, which may require non-tamper-resistant receptacles for compatibility and functionality.
What are alternative safety measures that can be implemented in locations where tamper-resistant receptacles are not required?
Alternative safety measures include the use of lockout/tagout procedures, proper signage, and training programs to educate personnel about electrical hazards.