Client-centered therapy its current practice implications and theory carl rogers – Client-centered therapy, pioneered by Carl Rogers, is a humanistic approach that emphasizes the client’s inherent capacity for growth and self-actualization. This article explores the theoretical underpinnings, techniques, applications, and current implications of client-centered therapy, providing a comprehensive understanding of its principles and practices.
1. Introduction
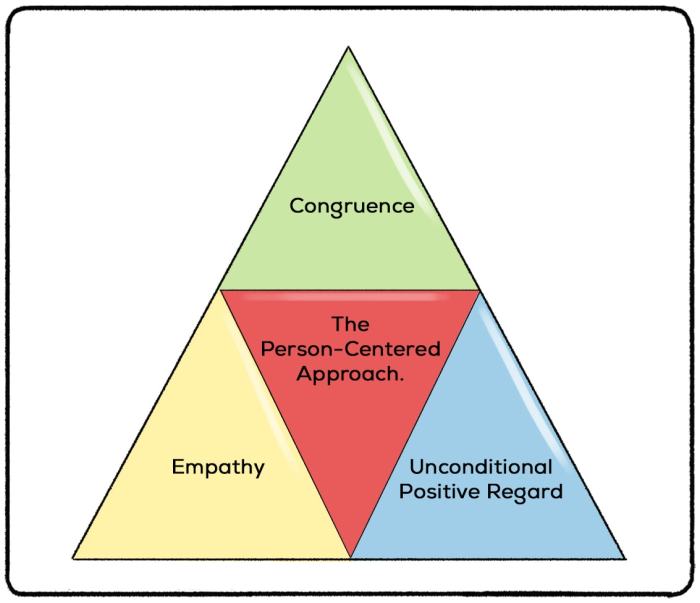
Client-centered therapy, also known as person-centered therapy, is a humanistic approach to psychotherapy that emphasizes the client’s subjective experience and self-directed growth.
It was developed by Carl Rogers in the 1940s and 1950s, and is based on the belief that individuals have the capacity for self-understanding, self-acceptance, and self-actualization.
The key principles of client-centered therapy include:
- The therapist’s unconditional positive regard for the client
- The therapist’s empathy for the client’s subjective experience
- The therapist’s facilitation of the client’s self-exploration and self-discovery
2. Theoretical Underpinnings of Client-Centered Therapy

Client-centered therapy is based on the principles of humanistic psychology, which emphasizes the importance of human potential, free will, and self-actualization.
Carl Rogers’ self theory is a key component of client-centered therapy. This theory proposes that individuals have a basic need for positive regard from others, and that this need can be met through unconditional positive regard from the therapist.
Unconditional positive regard is a non-judgmental and accepting attitude towards the client, regardless of their thoughts, feelings, or behaviors.
3. Techniques and Interventions in Client-Centered Therapy
Client-centered therapy uses a variety of techniques and interventions to facilitate the client’s self-exploration and self-discovery.
Active listening is a key technique in client-centered therapy. This involves the therapist paying close attention to the client’s verbal and non-verbal communication, and reflecting back what they hear in a way that demonstrates understanding and empathy.
Empathy is another important technique in client-centered therapy. This involves the therapist trying to understand the client’s subjective experience from the client’s own perspective.
Reflection is a technique that involves the therapist repeating back to the client what they have said, in order to help them to clarify their thoughts and feelings.
4. Applications of Client-Centered Therapy

Client-centered therapy can be used to treat a variety of mental health issues, including:
- Anxiety disorders
- Depression
- Eating disorders
- Personality disorders
- Relationship problems
Client-centered therapy can be used in individual therapy, group therapy, and couples therapy.
There is a strong evidence base for the effectiveness of client-centered therapy.
5. Criticisms and Limitations of Client-Centered Therapy
Client-centered therapy has been criticized for its lack of structure and its potential to be overly permissive.
Some critics argue that client-centered therapy is not effective for clients with severe mental health issues.
However, there is evidence to suggest that client-centered therapy can be effective for a wide range of mental health issues, including severe mental health issues.
Recommendations for addressing the criticisms and limitations of client-centered therapy include:
- Providing more structure to the therapy
- Setting clear goals for therapy
- Monitoring the client’s progress and making adjustments to the therapy plan as needed
FAQ: Client-centered Therapy Its Current Practice Implications And Theory Carl Rogers
What are the key principles of client-centered therapy?
The key principles include unconditional positive regard, empathy, and congruence.
How does client-centered therapy differ from other approaches?
Client-centered therapy focuses on the client’s subjective experience and emphasizes their capacity for self-growth, in contrast to approaches that prioritize external interventions or diagnosis.
What are the applications of client-centered therapy?
Client-centered therapy is used to address a wide range of mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, relationship problems, and personality disorders.