Embark on an enlightening journey with AP Psychology Unit 1 Flashcards, your ultimate companion for mastering the fundamentals of psychology. Dive into the captivating world of scientific inquiry, research methodologies, and the intricate biological underpinnings of human behavior. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of the human mind and unlock your potential for academic excellence.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with a solid understanding of the core concepts, research methods, and biological bases of behavior covered in AP Psychology Unit 1. With engaging examples and practical applications, you’ll gain invaluable insights into the fascinating field of psychology.
Key Concepts
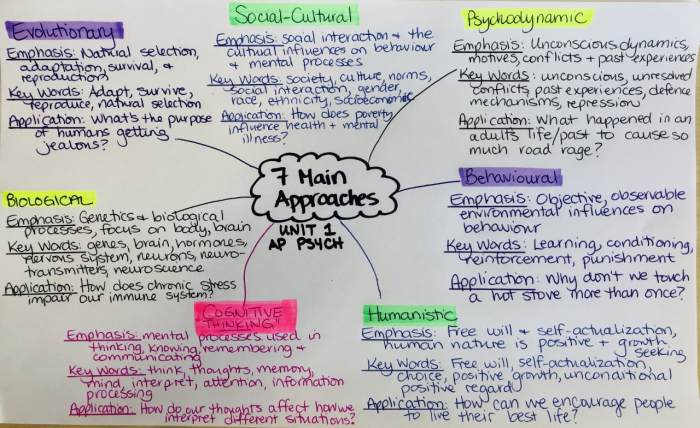
Psychology, as a scientific discipline, explores the intricate workings of the human mind and behavior. It employs rigorous research methods and leverages insights from biology to unravel the mysteries of human cognition, emotions, and actions.
Understanding the biological bases of behavior sheds light on the neural and physiological mechanisms that underpin our thoughts, feelings, and actions. This knowledge provides a foundation for comprehending psychological phenomena and developing effective interventions to address mental health challenges.
Cramming for AP Psychology Unit 1? Don’t forget about the ceretec white blood cell scan , a crucial concept in biological psychology. Understanding this scan will help you ace the exam and expand your knowledge of the human body’s intricate workings.
Back to Unit 1 flashcards – keep reviewing those research methods and ethical guidelines to nail the test!
Research Methods
Research methods are the cornerstone of scientific psychology, enabling researchers to gather data and test hypotheses about psychological phenomena. These methods include:
- Observational Methods:Observing and recording behaviors in natural or controlled settings without direct intervention.
- Experimental Methods:Manipulating variables to examine cause-and-effect relationships, ensuring greater control over the research environment.
- Correlational Methods:Examining relationships between variables without manipulating them, providing insights into potential associations but not establishing causation.
Biological Bases of Behavior
The biological bases of behavior encompass the physiological and neurological structures that influence our thoughts, feelings, and actions. Key concepts include:
- Neurons:Specialized cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the nervous system.
- Neurotransmitters:Chemical messengers that facilitate communication between neurons, influencing mood, cognition, and behavior.
- Brain Structures:Different regions of the brain, such as the amygdala and hippocampus, serve specific functions related to emotion, memory, and learning.
Research Methods: Ap Psychology Unit 1 Flashcards

In psychology, researchers use various methods to investigate human behavior and mental processes. These methods range from carefully controlled experiments to in-depth case studies, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Experiments
Experiments are the gold standard of psychological research, allowing researchers to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher manipulates one or more independent variables and measures the effect on one or more dependent variables while controlling for other factors that could influence the results.
Strengths:
- High internal validity: Experiments allow researchers to isolate and control variables, reducing the likelihood of confounding factors influencing the results.
- Can establish causality: By manipulating the independent variable, researchers can determine whether it causes changes in the dependent variable.
Limitations:
- Low external validity: Experiments are often conducted in controlled laboratory settings, which may not generalize to real-world situations.
- Artificiality: The controlled environment of an experiment can create artificial conditions that may not reflect natural behavior.
Examples:
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Demonstrated the powerful effects of situational factors on human behavior.
- The Marshmallow Test: Investigated the role of self-control in academic and life success.
Biological Bases of Behavior
The biological perspective in psychology focuses on how our physical makeup, particularly our brain and nervous system, influences our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. This perspective has led to significant advancements in understanding the relationship between biology and behavior, opening up new avenues for research and treatment.
Role of the Nervous System and Endocrine System
The nervous system is a complex network of cells that transmit information throughout the body. It consists of the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which connects the CNS to the rest of the body.
The CNS is responsible for processing information, making decisions, and controlling movement, while the PNS relays sensory information from the body to the CNS and sends motor commands from the CNS to the muscles and glands.The endocrine system is a network of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
Hormones are chemical messengers that travel throughout the body and influence a wide range of physiological and psychological processes, including growth, metabolism, mood, and reproduction.
Genetics and Environmental Factors
Genetics play a significant role in shaping our physical characteristics and predispositions, including our brain development and behavior. Genes provide the instructions for building and maintaining our bodies, and they influence our susceptibility to certain disorders and diseases. However, genetics alone do not determine our behavior; environmental factors also have a profound impact.Environmental
factors, such as prenatal nutrition, early childhood experiences, and social interactions, can shape brain development and influence our behavior throughout life. For example, research has shown that children who experience neglect or abuse are more likely to develop mental health problems later in life.
Disorders that Illustrate the Relationship Between Biology and Behavior
Numerous disorders illustrate the relationship between biology and behavior. For example, schizophrenia is a mental illness characterized by hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking. Research has shown that schizophrenia is associated with abnormalities in brain structure and function, as well as genetic factors.Another
example is Alzheimer’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that leads to memory loss and cognitive decline. Alzheimer’s disease is caused by the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, which disrupt neuron function and communication.These disorders demonstrate how biological factors can contribute to the development of psychological problems, highlighting the importance of understanding the biological bases of behavior.
Applications of Psychology
Psychology’s principles have broad applications in various fields, including education, healthcare, and business. By understanding human behavior, psychologists can help improve learning, promote well-being, and enhance organizational effectiveness.
Education, Ap psychology unit 1 flashcards
- Cognitive psychologyinforms teaching methods, such as spaced repetition and interleaving, to enhance memory and learning.
- Developmental psychologyguides curriculum design and instructional strategies tailored to students’ developmental stages.
- Social psychologypromotes positive classroom dynamics, conflict resolution, and peer support.
Healthcare
- Clinical psychologyprovides therapy for mental health disorders, helping individuals overcome challenges and improve well-being.
- Health psychologyfocuses on the psychological factors that influence health and illness, promoting healthy behaviors and coping mechanisms.
- Neuropsychologyassesses and treats cognitive impairments resulting from brain injuries or neurological disorders.
Business
- Industrial-organizational psychologyoptimizes workplace environments, improves employee motivation, and enhances productivity.
- Consumer psychologyunderstands consumer behavior, influencing marketing strategies and product design.
- Human factors psychologydesigns user interfaces and products that are safe, efficient, and user-friendly.
Psychology’s applications have profoundly improved people’s lives. For example, cognitive training programs based on research have enhanced memory in older adults. Mindfulness-based interventions have reduced stress and improved mental well-being. Organizational psychology has increased employee satisfaction and reduced turnover rates.
These applications demonstrate the practical relevance and transformative impact of psychology in various aspects of our lives.
FAQ Guide
What are the key concepts covered in AP Psychology Unit 1?
AP Psychology Unit 1 delves into the core concepts of psychology as a science, research methods, and the biological bases of behavior.
How can I use these flashcards effectively?
Regularly review the flashcards, engage in active recall by trying to answer the questions without looking at the answers, and utilize them as a study tool before exams.
Are there any additional resources available for AP Psychology Unit 1?
Yes, there are numerous online resources, textbooks, and study guides that can supplement your learning.